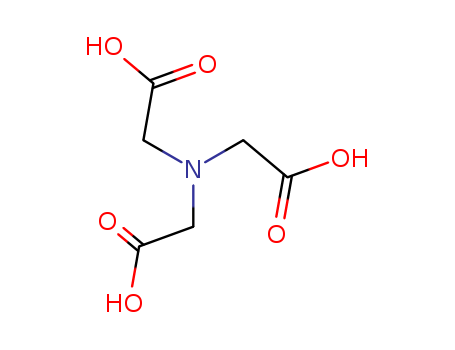

CasNo: 139-13-9
Molecular Formula: C6H9NO6
Appearance: white powder
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 15, p. 46, 1950 DOI: 10.1021/jo01147a008 |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Water Insoluble. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Nitrilotriacetic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizers, aluminum, copper, copper alloy and nickel. Nitrilotriacetic acid is also incompatible with strong bases. |
|
Hazard |
Possible carcinogen. |
|
Health Hazard |
Toxicity and health hazard of these compounds are low. Contact with eyes causes irritation. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Nitrilotriacetic acid are not available; however, Nitrilotriacetic acid is probably combustible. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Nitrilotriacetic (NTA) has the ability to link with histidine side chain of proteins. It can be used in fluorescent labelling, hexahistidine (His6)-tagged proteins for purification and surface immobilization. |
|
Safety Profile |
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) was used as a phosphate replacement in laundry detergents in the late 1960s. In 1971, the use of NTA was discontinued. The possibility of resumed use arose in 1980. NTA is now used in laundry detergents in states where phosphates are banned. NTA is also used as a boiler feed-water additive at a maximum use level of 5 ppm of trisodium salt. Currently, the remaining nondetergent uses of NTA are for water treatment, textile treatment; metal plating and cleaning; and pulp and paper processing. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
Nitrilotriacetic acid is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals. |
|
Shipping |
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise it from water and dry it at 110o. [Beilstein 4 IV 2441.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur). Attacks aluminum, copper, copper alloy and nickel. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed. |
|
General Description |
Odorless white solid. Sinks in and mixes with water. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H9NO6/c8-4(9)1-7(2-5(10)11)3-6(12)13/h1-3H2,(H,8,9)(H,10,11)(H,12,13)
-
-
The present invention relates to a proce...
To enable measurements having high S/N r...
This invention relates to biochemistry a...
A self-assembled relay probe for detecti...
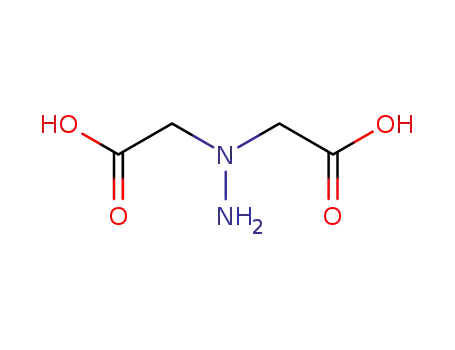
N,N-dicarboxymethyl hydrazine

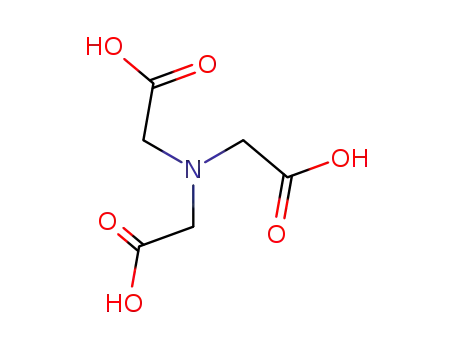
nitrilotriacetic acid
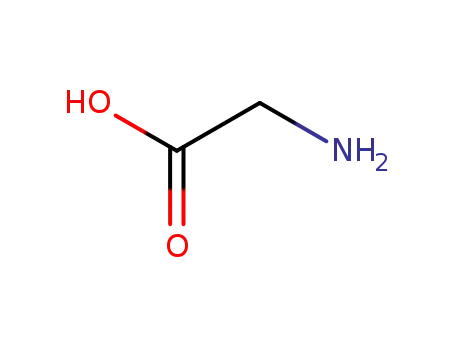
glycine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
beim Erhitzen;
|
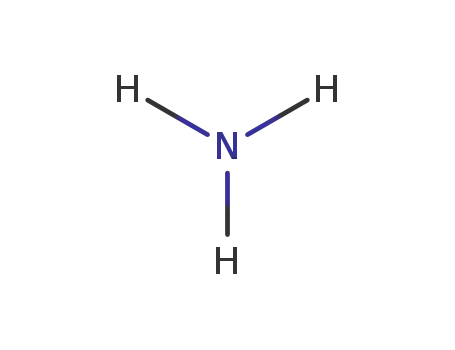
ammonia

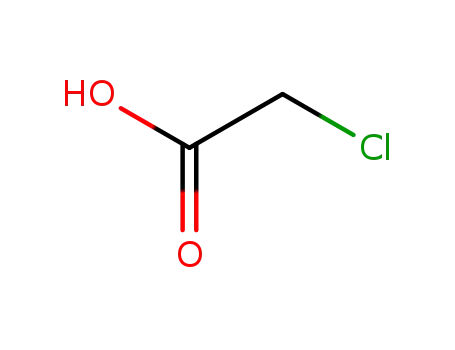
chloroacetic acid


nitrilotriacetic acid


glycine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
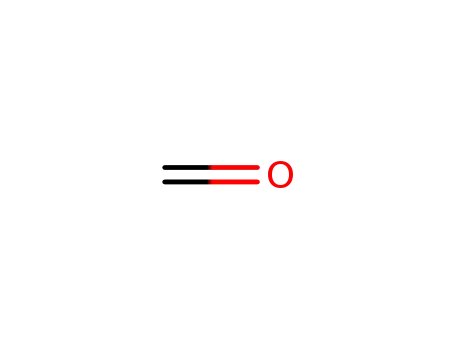
formaldehyd
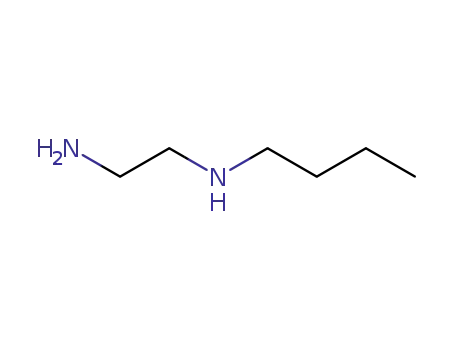
N-butylethylenediamine
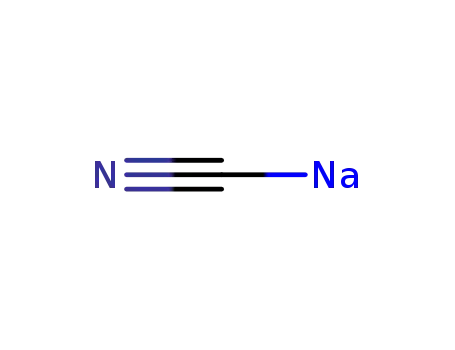
sodium cyanide
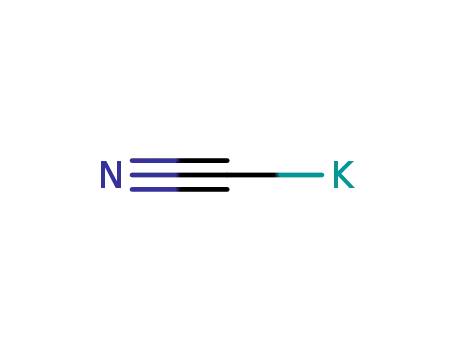
potassium cyanide
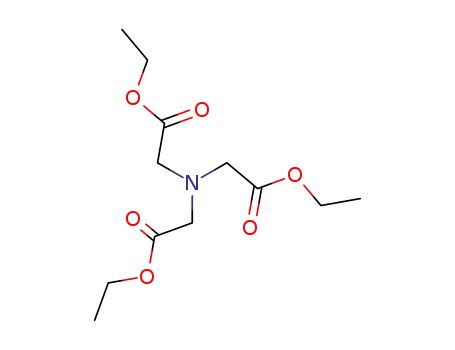
triethyl nitrilotriacetate
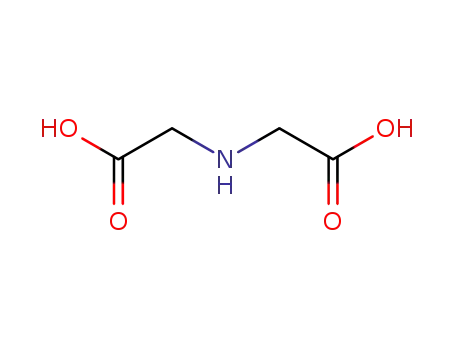
iminodiacetic acid
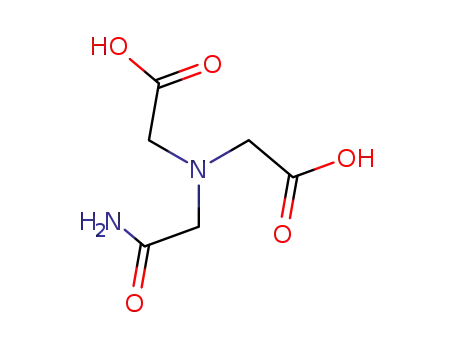
N-(2-acetamido)-3-iminodiacetic acid
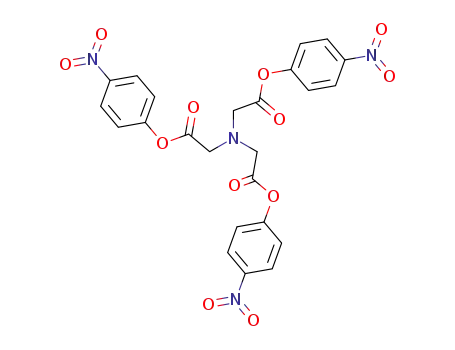
nitrilotriacetic acid tris(p-nitrophenyl ester)
CAS:148893-10-1
CAS:24980-41-4
CAS:3658-77-3