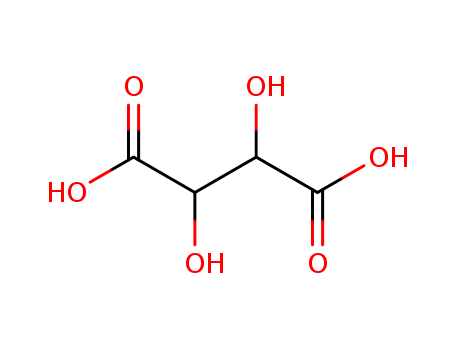

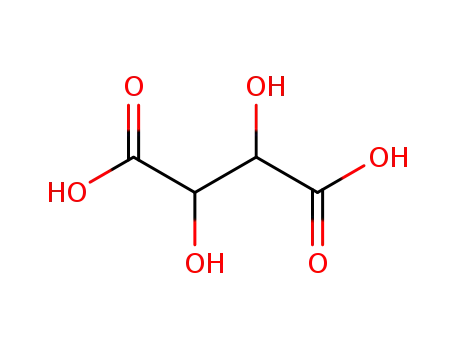
CasNo: 526-83-0
Molecular Formula: C4H6O6
Appearance: white crystalline diprotic organic acid
|
Definition |
A crystalline naturallyoccurring carboxylic acid,(CHOH)2(COOH)2; r.d. 1.8; m.p.171–174°C. It can be obtained fromtartar (potassium hydrogen tartrate)deposits from wine vats, and is usedin baking powders and as a foodstuffsadditive. The compound isoptically active (see optical activity).The systematic name is 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid. |
|
Derivatives |
Important derivatives of tartaric acid include its salts, cream of tartar (potassium bitartrate), Rochelle salt (potassium sodium tartrate, a mild laxative), and tartar emetic (antimony potassium tartrate). Diisopropyl tartrate is used as a catalyst in asymmetric synthesis.Tartaric acid is a muscle toxin, which works by inhibiting the production of malic acid, and in high doses causes paralysis and death. The median lethal dose (LD50) is about 7.5 grams / kg for a human, ~5.3 grams/kg for rabbits and ~4.4 grams/kg for mice . Given this figure, it would take over 500 g to kill a person weighing 70 kg , and so it may be safely included in many foods, especially sour-tasting sweets. As a food additive, tartaric acid is used as an antioxidant with E number E334, tartrates are other additives serving as antioxidants or emulsifiers. . |
|
Stereo chemistry |
Naturally occurring tartaric acid is chiral, meaning it has molecules that are not superimposable on their mirror images. It is a useful raw material in organic chemistry for the synthesis of other chiral molecules. The naturally occurring form of the acid is L-(+)- tartaric acid or dextrotartaric acid. The mirror-image (enantiomeric) form, levotartaric acid or D-(?)-tartaric acid, and the achiral form, mesotartaric acid, can be made artificially. The dextro and levo prefixes are not related to the D/L configuration (which is derived rather indirectly[8] from their structural relation to D- or L-glyceraldehyde), but to the orientation of the optical rotation, (+) = dextrorotatory, (?) = levorotatory. Sometimes, instead of capital letters, small italic d and l are used. They are abbreviations of dextroand levo- and, nowadays, should not be used. Levotartaric and dextrotartaric acid are enantiomers, mesotartaric acid is a diastereomer of both of them.Tartaric acid is used to prevent copper(II) ions from reacting with the hydroxide ions present in the preparation of copper(I) oxide. Copper(I) oxide is a reddish-brown solid, and is produced by the reduction of a Cu(II) salt with an aldehyde, in an alkaline solution. |
|
Tartaric acid in wine |
Tartaric acid may be most immediately recognizable to wine drinkers as the source of "wine diamonds", the small potassium bitartrate crystals that sometimes form spontaneously on the cork. These "tartrates" are harmless, despite sometimes being mistaken for broken glass, and are prevented in many wines through cold stabilization. The tartrates remaining on the inside of aging barrels were at one time a major industrial source of potassium bitartrate. However, tartaric acid plays an important role chemically, lowering the pH of fermenting "must" to a level where many undesirable spoilage bacteria cannot live, and acting as a preservative after fermentation. In the mouth, tartaric acid provides some of the tartness in the wine, although citric and malic acids also play a role. |
InChI:InChI=1/C4H6O6/c5-1(3(7)8)2(6)4(9)10/h1-2,5-6H,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)
The nano-composites Fe3O4SiO2(-O3Si[(CH2...
The present invention is related to a ca...
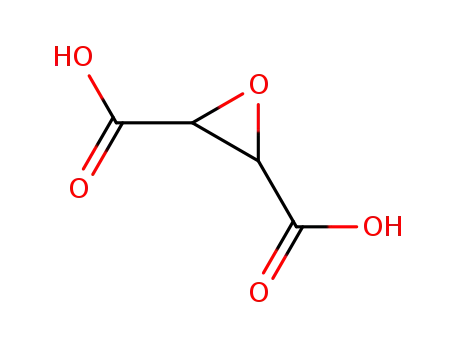
2,3-oxiranedicarboxylic acid

L-tartaric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
epoxide hydrolase;
|
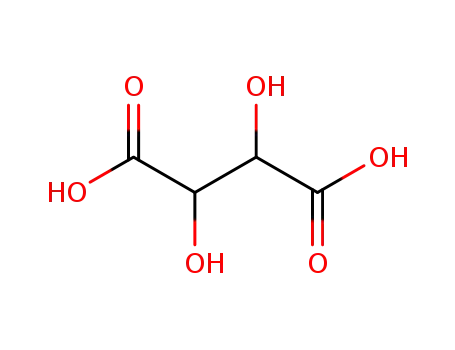
tartaric acid

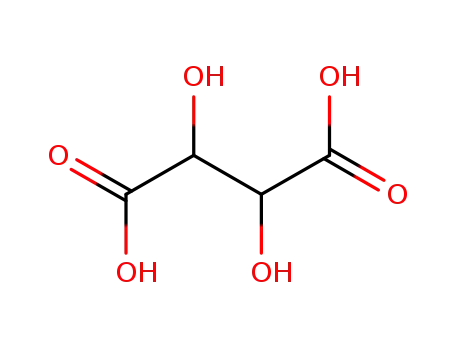
(-)-D-tartaric acid
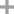
L-(+)-tartaric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
(+)-enantiomer of phosphoric triamide deposited on Fe3O4/silica nanoparticle;
In
methanol; water;
for 1h;
Resolution of racemate;
|
19 % ee |
|
With
(-)-enantiomer of phosphoric triamide deposited on Fe3O4/silica nanoparticle;
In
methanol; water;
for 1h;
Resolution of racemate;
|
18 % ee |

2,3-oxiranedicarboxylic acid

tartaric acid
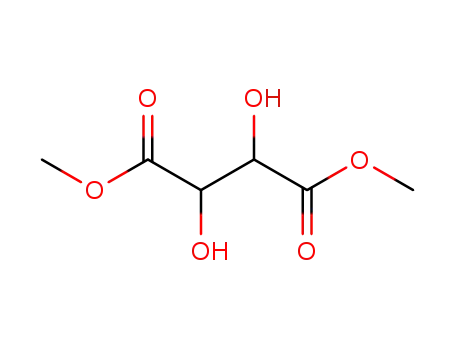
dimethyl L-tartrate
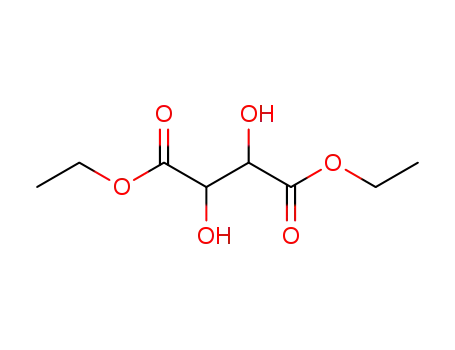
diethyl L-tartrate
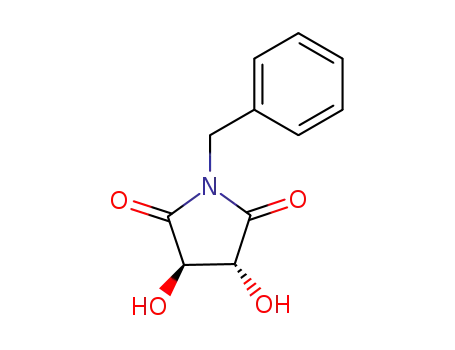
(3R,4R)-1-benzyl-3,4-dihydroxypyrrolidine-2,5-dione
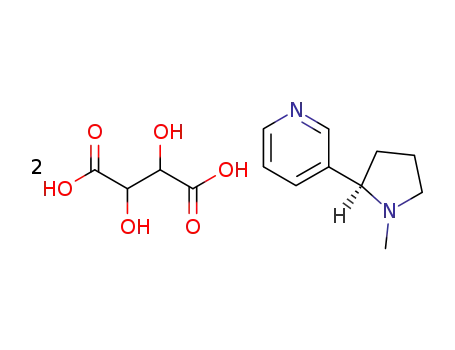
(+)-Nicotine bitartrate
CAS:148893-10-1
CAS:106809-14-7
CAS:184719-80-0