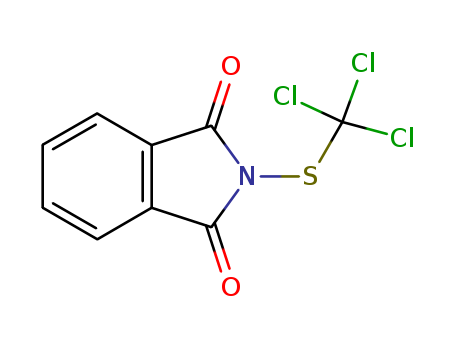

CasNo: 133-07-3
Molecular Formula: C9H4Cl3NO2S
Appearance: White crystals
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. Hydrolyzed in alkaline solution. Hydrolysis products are corrosive to many metals. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
A halogenated phthalimide. |
|
Contact allergens |
Folpet is a pesticide, fungicide agent of thiophthalim ide group. Occupational exposure occurs mostly in agricultural workers or in florists. Photosensitivity has been reported. |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic and teratogenic data. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl-, NOx, and SOx. Used as a fungicide. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
An NCI bioassay of technicalgrade captan was conducted to determine carcinogenicity by administering captan in the feed to Osborne–Mendel rats and B6C3F1 mice. The major outcome was that tumors of the duodenum of B6C3F1 mice were associated with the captan treatment. There was no evidence that the tumors observed in Osborne–Mendel rats were treatment-related. In the NCI study, groups of 50 rats of each sex were fed average doses of 2520 or 6050 ppm captan in the diet for 80 weeks. Groups of 50 mice of each sex were fed 8000 or 16,000 ppm captan in the diet for 80 weeks. These doses are approximately 250 (male) and 450 (female) mg/kg/day (high dose) and 50 (male) to 100 (female) mg/kg/day (low dose) in rats. In mice, these doses are approximately 2100 mg/kg/day (high dose) and 1000 mg/kg/day (low dose). |
|
Environmental Fate |
Folpet rapidly degrades in both aquatic and terrestrial environments, with a reported half-life ranging from 2.6 h to 2 days. The dissipation of folpet in the environment is considered to be dependent on its hydrolysis in water and on microbial-mediated degradation. Its rate of hydrolysis is greatly influenced by pH, with more rapid hydrolysis observed at higher, more alkaline pH levels. |
|
Metabolic pathway |
Folpet contains an unstable trichloromethylthio (sulfenyl) moiety that has been shown to undergo rapid hydrolytic and metabolic degradation to phthalimide (2). By analogy with captan, presumably the trichloromethylthio moiety can be transferred to the sulfur atoms of thiols such as cysteine and glutathione. Thus in the presence of thiols such as glutathione, folpet is probably cleaved at the N-S bond to form thiophosgene (3) and other gaseous products such as hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen chloride and carbonyl sulfide. Thiophosgene (3) is rapidly hydrolysed by water. The trichloromethylthio group and thiophosgene are believed to be intermediates in the formation of thiazolidine-2-thione-4-carboxylica cid (4) which is an addition product with cysteine. A thiazolidine derivative of glutathione may also be formed (5). Folpet is metabolised in plants and animals to phthalimide (2) and further to phthalamic acid (6) and phthalic acid (7) (see Scheme 1). |
|
Degradation |
Folpet is hydrolysed rapidly in strongly alkaline conditions (PM). The hydrolytic DT50 of folpet is 1.1 hours at pH 7. The half-life for hydrolysis of folpet in a commercial formulation was 12 hours at pH 7.35. Folpet was decomposed in dilute, aqueous sulfuric acid with a half-life 10.5 hours at pH 3. The products were mainly phthalimide (2) and small amounts of phthalamic acid (6) and phthalic acid (7). Phthalamic acid (6) had completely degraded by the time all of the folpet had decomposed (Cabras et al., 1997). Folpet reacts with thiols in two steps. Firstly, phthalimide (2), thiophosgene (3), hydrochloric acid and the corresponding disulfide are produced. Secondly, depending on the thiol, thiophosgene (3) can react with any remaining thiols to give trithiocarbonates, thiurams, etc. In some cases as, for example, with L-cysteine, thiophosgene (3) combines with amino and thiol groups of the reactant yielding the cyclic 2- thiazolidinethiones (4) (Davidek and Seifert, 1975). Folpet reacts with reduced glutathione (GSH) to produce mainly oxidised glutathione (GSSG). Five unidentified products contained all or a portion of the trichloromethyl moiety. Gaseous products including carbonyl sulfide were released (Siegel, 1970). |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
Both folpet and its reactive metabolite, thiophosgene, interact with thiol groups and denature proteins. This reaction is responsible for its fungicidal/biocidal activity and its cellular toxicity in mammals. Due to the toxicokinetics of this degradation, folpet toxicity in mammals is generally limited to local irritation effects at the site of contact. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A member of the class of phthalimides that is phthalimide in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a trichloromethylthio group. An agricultural fungicide, it has been used to control mildew, leaf spot, and other diseases in crops sice he 1950s. |
|
General Description |
White crystals. Used as a fungicide. Insoluble in water. |
InChI:InChI=1/C9H4Cl3NO2S/c10-9(11,12)16-13-7(14)5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8(13)15/h1-4H
-
The title compound (C9H4Cl3NO2S), common...
The present invention relates to a fungi...
Solvent-free coating materials and treat...
Wood preservatives having biocidal prope...
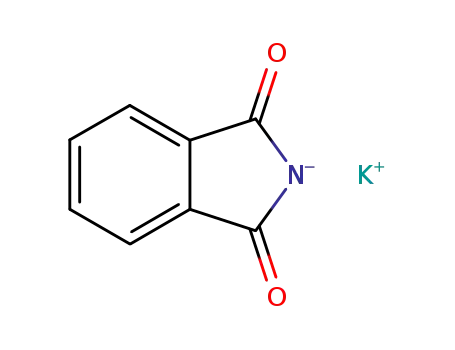
potassium phtalimide
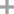
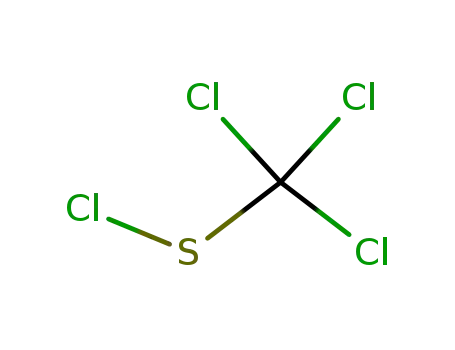
chlorothio-trichloro-methane

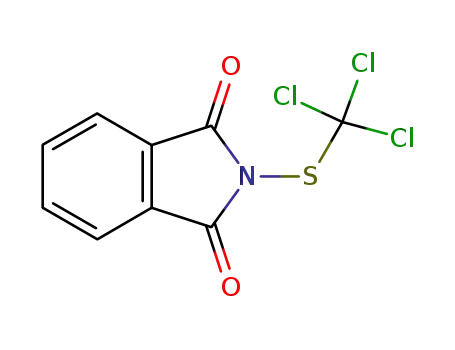
2-trichloromethylthio-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
benzene;
at 50 - 60 ℃;
|
|
|
With
benzene;
at 50 - 60 ℃;
|
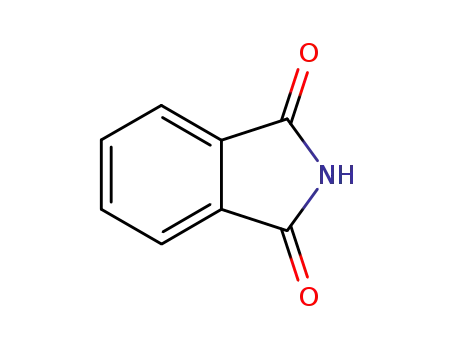
phthalimide


chlorothio-trichloro-methane


2-trichloromethylthio-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
phthalimide;
With
sodium hydroxide;
In
water;
at 10 - 15 ℃;
chlorothio-trichloro-methane;
In
water; toluene;
at 10 - 15 ℃;
|
70% |
|
With
triethylamine;
In
N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|

potassium phtalimide

chlorothio-trichloro-methane

phthalimide
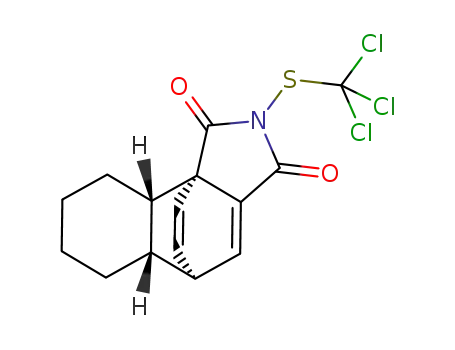
C15H14Cl3NO2S
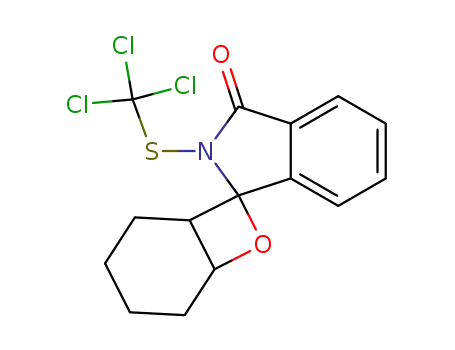
C15H14Cl3NO2S
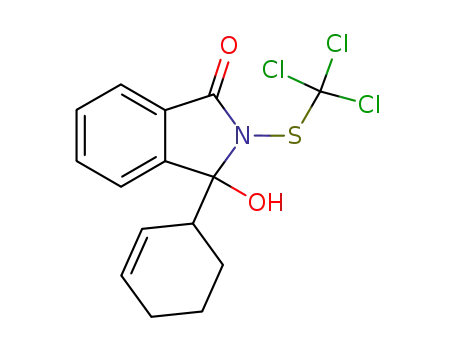
3-Cyclohex-2-enyl-3-hydroxy-2-trichloromethylsulfanyl-2,3-dihydro-isoindol-1-one
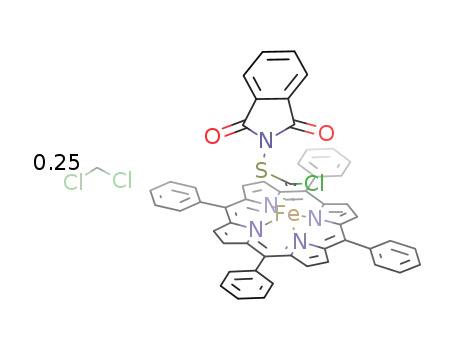
iron(II) tetraphenylporphyrin (thiophthalimido)chlorocarbene
CAS:30123-17-2
CAS:85-91-6
CAS:4674-50-4