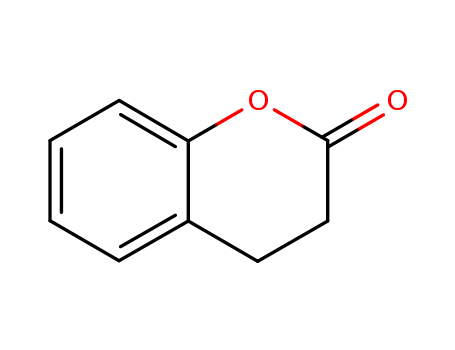

CasNo: 119-84-6
Molecular Formula: C9H8O2
Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow clear liquid
|
Sources |
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:16151 http://www.bojensen.net/EssentialOilsEng/EssentialOils29/EssentialOils29.htm#Tonka https://books.google.kg/books?id=pUEqBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA427&lpg=PA427&dq=dihydrocoumarin+uses&source=bl&ots=HTZrffvsXu&sig=GPGKqrMRXQaRJ-qgHk7aULeBmGw&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=dihydrocoumarin%20uses&f=false https://products.symrise.com/aroma-molecules/product-search/dihydrocoumarin/action/pdf/ http://www.lookchem.com/3-4-Dihydrocoumarin/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1315280/ |
|
Preparation |
Dihydrocoumarin is synthesized by reduction of coumarin under pressure in the presence of nickel at 160 to 200°C or in the presence of Pd-BaSO4 in alcoholic solution. |
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
Tetrahedron Letters, 37, p. 4555, 1996 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(96)00902-1 |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Solutions of the chemical in water are stable for less than two hours. Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Hydrocoumarin is a lactone (behaves as an ester). Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Hydrocoumarin may hydrolyze under alkaline or acidic conditions. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Hydrocoumarin is combustible. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Taste at 10 ppm |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A chromanone that is the 3,4-dihydro derivative of coumarin. |
|
General Description |
White to pale yellow clear oily liquid with a sweet odor. Solidifies around room temperature. |
InChI:InChI=1/C9H8O2/c10-9-6-5-7-3-1-2-4-8(7)11-9/h1-4H,5-6H2
The production of octahydrocoumarin, whi...
-
The homoleptic organocerium complex Ce{C...
An efficient method has been developed f...
A nickel-catalysed electroreductive proc...
Dihydrocoumarins are obtained in 40 to 6...
Palladium nanoparticles stabilised by N-...
The hydrogenation of a number of oxygen-...
Hydrotalcites promote the Baeyer-Villige...
-
Addition of α-fluoro ethers to cyclohexa...
The combination of chemical and biologic...
A theoretical investigation of model mec...
The ionic liquids, BMIM PF6 or BMIM NTf2...
-
The invention discloses an industrial pr...
Direct hydrogen atom transfer from a pho...
A widely applicable approach was develop...
The invention relates to a hydrogenation...
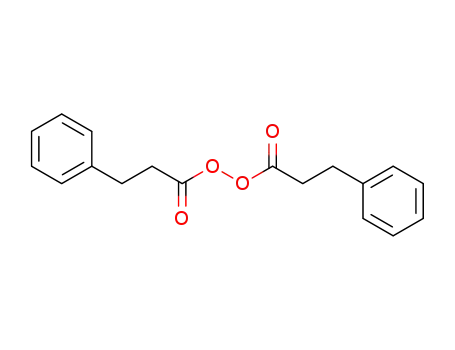
β-phenylpropionyl peroxide

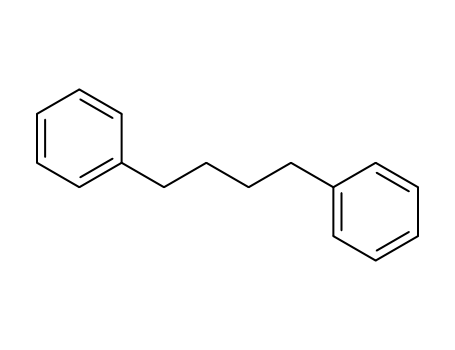
1,4-diphenylbutane
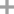
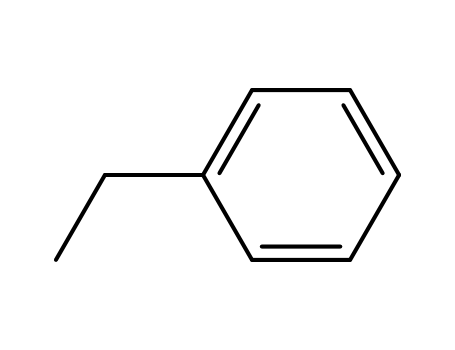
ethylbenzene

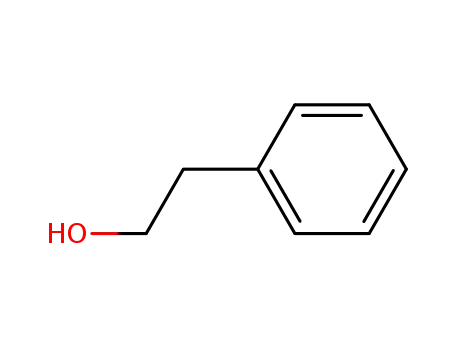
2-phenylethanol

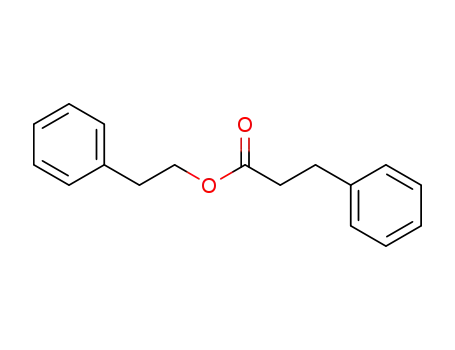
3-phenylpropionic acid 2-phenylethyl ester

C6H4(CH2CH2C(O)O)

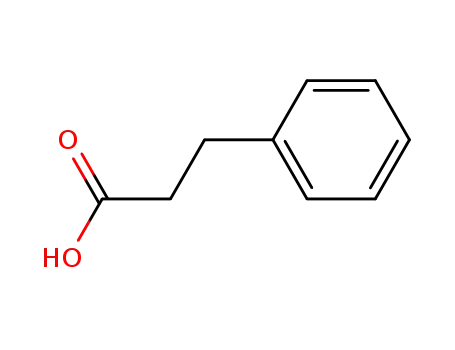
3-Phenylpropionic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
P0 silica;
at 55 ℃;
Rate constant;
Product distribution;
coadsorbed O2, photolysis, other temperatures;
|
48.4% 18.2 % Chromat. 2.04 % Chromat. 0.63 % Chromat. 9.3 % Chromat. 3.92 % Chromat. |
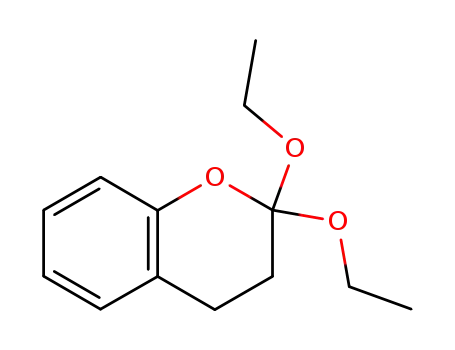
diethoxy-2,2 benzopyranne-1

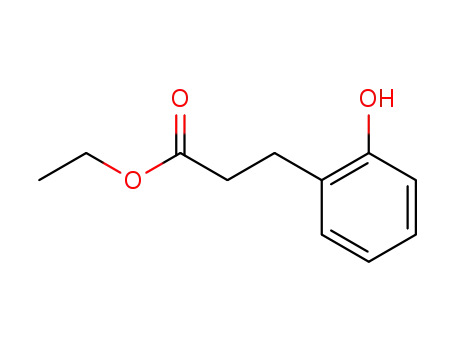
ethyl 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate

C6H4(CH2CH2C(O)O)
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
formic acid;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 25.2 ℃;
Rate constant;
Thermodynamic data;
var. acid catalysts, var. pH, catalytic constants, ΔH(excit.), ΔS(excit.);
|
96 % Spectr. 4 % Spectr. |
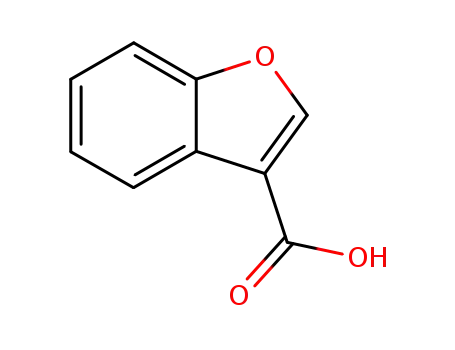
benzofurane-3-carboxylic acid
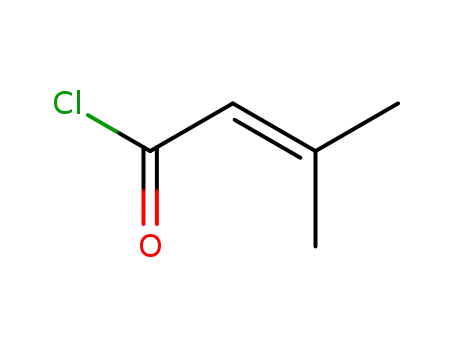
3,3-Dimethylacryloyl chloride
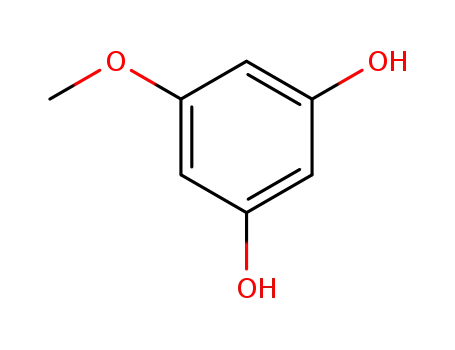
5-methoxyresorcinol
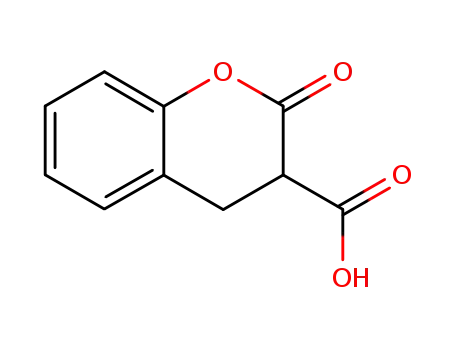
2-oxochroman-3-carboxylic acid
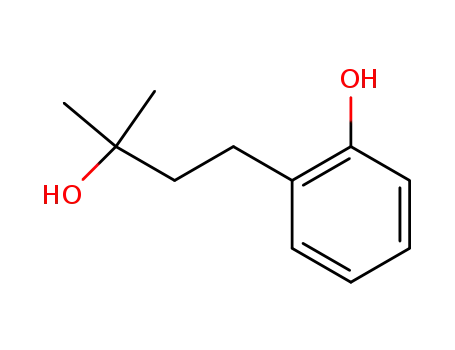
4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-butanol
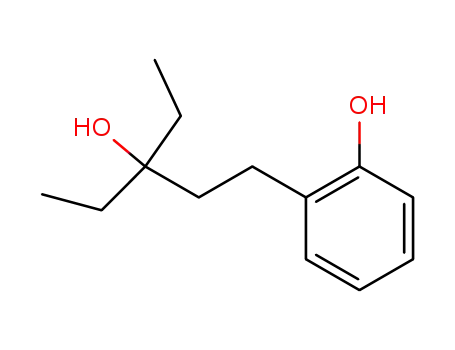
3-ethyl-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-pentanol
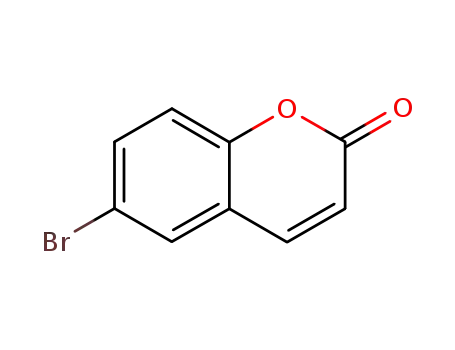
6-bromo-2H-chromen-2-one
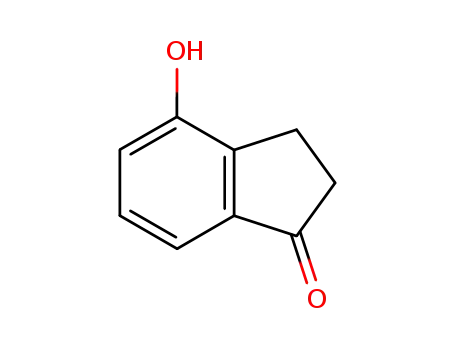
4-hydroxy-2,3-dihydroindan-1-one
CAS:148893-10-1
CAS:10222-01-2
CAS:16816-67-4