
CasNo: 73-22-3
Molecular Formula: C11H12N2O2
Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder
|
Essential Amino Acid |
Tryptophan (TRP) is an essential amino acid in mammals, crucial for various physiological processes such as neuronal function, immunity, and gut homeostasis. |
|
Chemical Structure and Classification |
Tryptophan is the largest of the three aromatic amino acids, with a benzoic nucleus and a pyrrole ring in its side chain. It has the molecular formula C11H12N2O2 and is categorized as a glucogenic/ketogenic amino acid. |
|
Dietary Sources and Absorption |
Being essential, TRP must be obtained through the diet. Rich dietary sources include dairy products, eggs, meat, fish, and chocolate. After being released from dietary protein, TRP is absorbed through the intestinal epithelium into the systemic circulation, where intestinal microbiota further metabolizes it to indoles. |
|
Physiological Effects |
TRP serves as a precursor for metabolites that significantly affect various physiological functions, including gastrointestinal functions, immunity, metabolism, and the nervous system. |
|
Binding and Regulation |
In circulation, TRP is primarily bound to albumin, with only a small fraction being free. Plasma TRP levels are regulated by factors such as glucocorticoids, interferon-纬, glucose, nicotinamide, and antidepressants. |
|
Implications in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders |
Changes in circulating TRP levels can impact its availability for serotonin and melatonin synthesis in the brain, potentially contributing to the pathophysiology of various neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. |
|
Role in Cancer and Immunoregulation |
TRP metabolism has been implicated in cancer-related processes, including anti-proliferative effects on tumor cells and cancer-related anorexia and cachexia. Research is ongoing regarding the immunoregulatory properties of IDO and its involvement in diseases such as autoimmunity, infection, and cancer. |
|
General Description |
L-Tryptophane is an essential amino acid that serves as a precursor for the synthesis of serotonin and melatonin, which play important roles in regulating mood and sleep. It is found in a variety of protein-rich foods such as turkey, chicken, fish, and dairy products, and is also available as a dietary supplement. L-Tryptophane has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects in treating depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders, and has also been investigated for its role in supporting immune function and promoting healthy digestion. However, |
InChI:InChI=1/C11H12N2O2/c12-9(11(14)15)5-7-6-13-10-4-2-1-3-8(7)10/h1-4,6,9,13H,5,12H2,(H,14,15)/t9-/m0/s1
N-demethylases have been reported to rem...
Abstract: The emergence of resistance to...
Separation of racemic mixtures is of gre...
Motobamide (1), a new cyclic peptide con...
![N-{(4-{methyl[(4-nitrophenoxy)carbonyl]amino}benzyloxy)carbonyl}-L-tryptophan](/upload/2025/3/f9577d44-b9b1-4de1-a0cf-9b5ce4041d79.png)
N-{(4-{methyl[(4-nitrophenoxy)carbonyl]amino}benzyloxy)carbonyl}-L-tryptophan

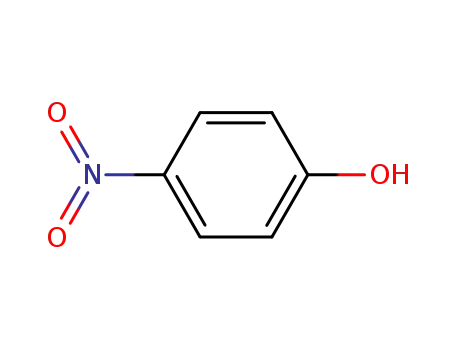
4-nitro-phenol
carbon dioxide

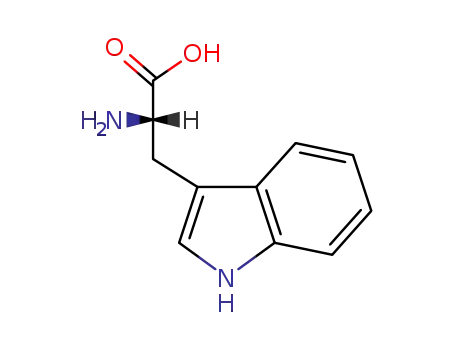
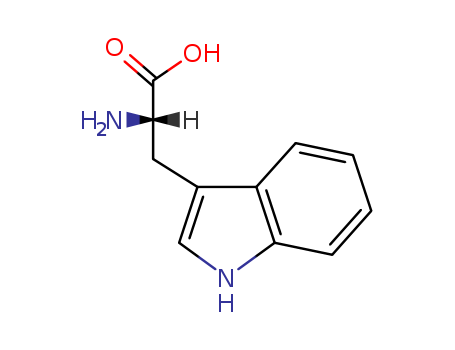
L-Tryptophan

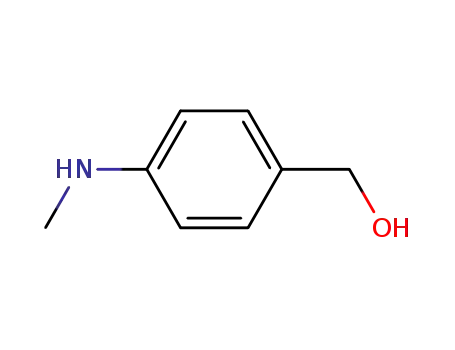
(4-(methylamino)phenyl)methanol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
abzyme ST51; water;
In
dimethyl sulfoxide;
at 25 ℃;
pH=9.0;
Further Variations:;
time dependence;
Enzyme kinetics;
|
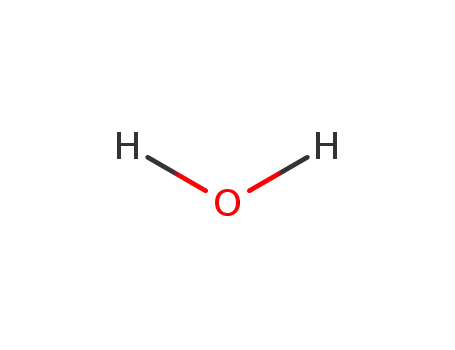
water

![[5']adenylic acid L-tryptophan anhydride](/upload/2025/3/7cbc77cc-2746-4486-b3ff-0a12ba153082.png)
[5']adenylic acid L-tryptophan anhydride

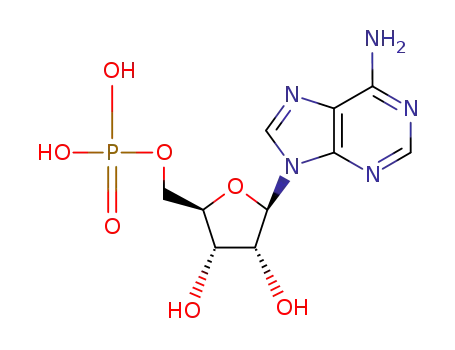
5'-adenosine monophosphate


L-Tryptophan
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 37 ℃;
Zeitlicher Verlauf in Loesung vom pH 7.2.Hydrolysis;
|
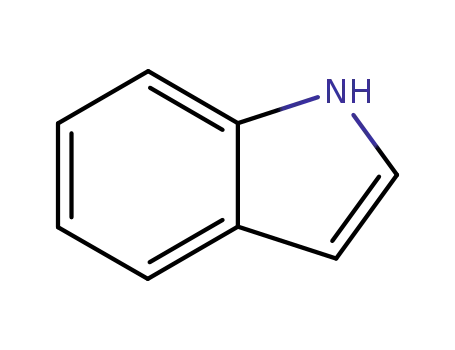
indole
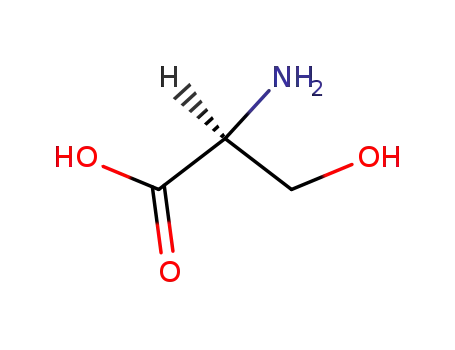
L-serin
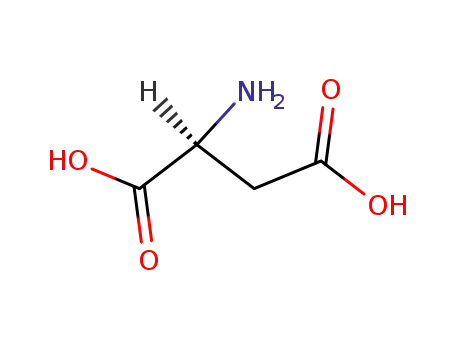
L-Aspartic acid
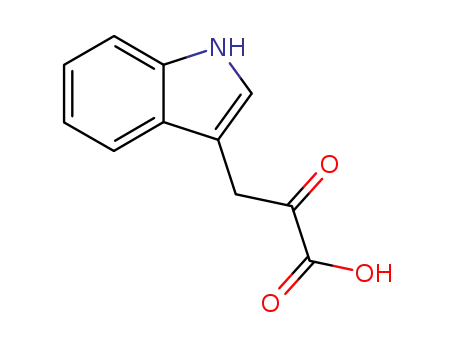
Indole-3-pyruvic acid
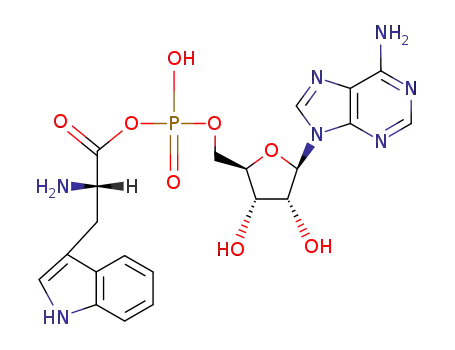
[5']adenylic acid L-tryptophan anhydride
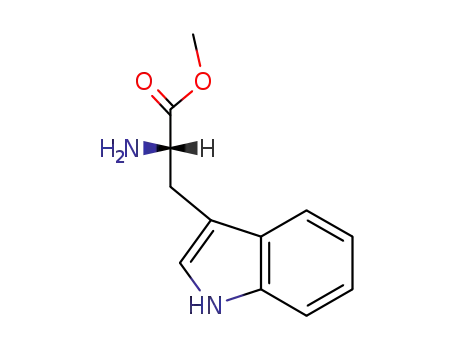
L-tryptophan methyl ester
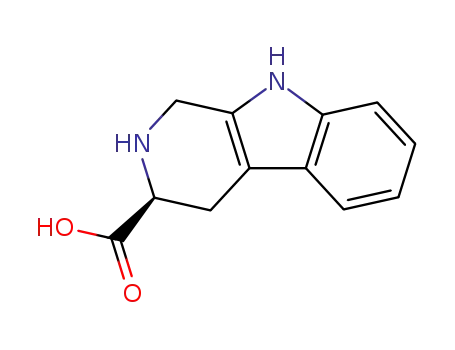
3-carboxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-carboline
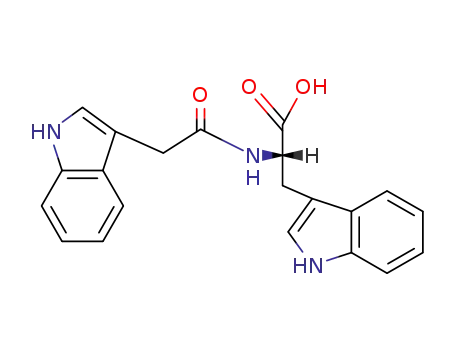
(2S)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-[(1H-indol-3-ylacetyl)amino]propanoic acid
CAS:148893-10-1
CAS:56-81-5
CAS:138261-41-3